命令(Command)模式是指将请求封装成为一个对象,使发出请求和执行请求的责任分割开,方便将命令对象进行存储、传递、调用、增加与管理。
也就是将发送者、接收者和调用命令封装成独立的对象,来供客户端调用。属于行为模式的一种。
一、命令模式介绍
命令模式将发送者与接受者完全解耦,发送者与接收者之间没有直接的联系,发送者只需要如何发送请求,而不需要关心请求是如何完成的。下面就来看看命令模式的结构和实现:
1.1 命令模式的结构
将调用者和实现者进行分离,其结构如下所示:
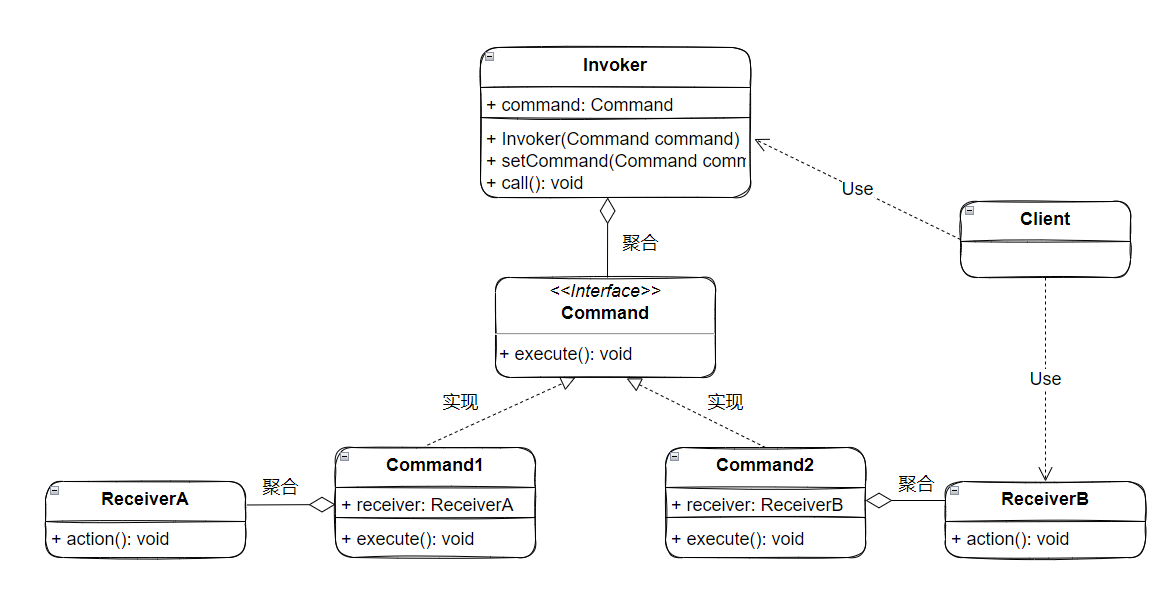
Command:抽象命令角色,声明执行命令的接口Command1、Command2:具体命令角色,是抽象命令角色的具体实现类ReceiverA、ReceiverB:具体实现,具体命令对象的真正实现者Invoker:调用者,处理命令、实现命令的具体操作者,负责对外提供命令服务Client:客户端
1.2 命令模式的实现
根据上面的结构图,可以实现如下代码:
/** * @description: 抽象命令类 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public interface Command { public abstract void execute(); } /** * @description: 命令具体实现类1 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class Command1 implements Command{ private ReceiverA receiverA = new ReceiverA(); @Override public void execute() { receiverA.action(); } } /** * @description: 命令具体实现类2 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class Command1 implements Command{ private ReceiverA receiverA = new ReceiverA(); @Override public void execute() { receiverA.action(); } } /** * @description: 接收者类A * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class ReceiverA { public void action() { System.out.println("我是ReceiverA"); } } /** * @description: 具体实现者 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class ReceiverB { public void action() { System.out.println("我是ReceiverB"); } } /** * @description: 命令调用者 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class Invoker { private Command command; public Invoker(Command command) { this.command = command; } public void setCommand(Command command) { this.command = command; } public void call() { System.out.println("调用者执行命令command"); command.execute(); } } /** * @description: 客户端 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { Command command1 = new Command1(); Invoker invoker1 = new Invoker(command1); invoker1.call(); } }最后的客户端运行结果为:
调用者执行命令command 我是ReceiverA下面来看看命令模式的应用场景
二、命令模式的应用场景
2.1 Spring 框架中的 JdbcTemplate
本文选取的Spring版本是5.3.1,来看看JdbcTemplate类中的query()方法:
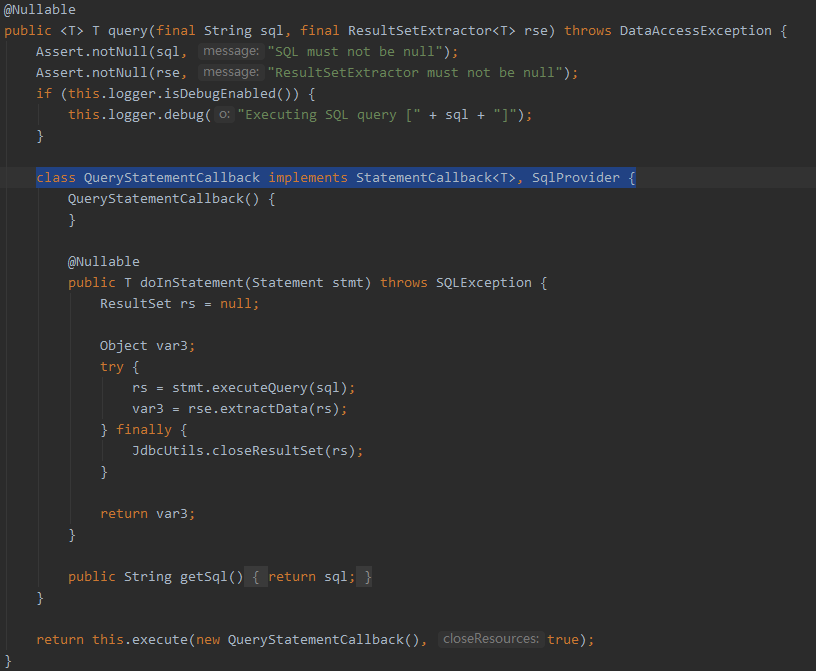
我们看到,上面的query()方法中定义了一个内部类QueryStatementCallback,并实现了StatementCallback接口,点开查看详细内容:
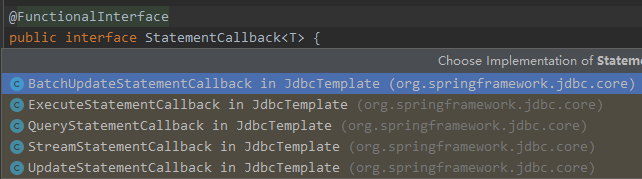
@FunctionalInterface public interface StatementCallback { //唯一的抽象方法 @Nullable T doInStatement(Statement var1) throws SQLException, DataAccessException; } 回到query()方法中,我们发现最后返回的execute(new QueryStatementCallback())中是将内部类QueryStatementCallback当做参数进行返回。这里QueryStatementCallback就相当于命令模式中的具体命令对象,而StatementCallback则是抽象命令对象。比如还有其他具体命令实现类,比如BatchUpdateStatementCallback、ExecuteStatementCallback等等:
看看execute()方法,为了方便理解,代码做了精简:
@Nullable private T execute(StatementCallback action, boolean closeResources) throws DataAccessException { Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.obtainDataSource()); Statement stmt = null; Object var12; try { stmt = con.createStatement(); this.applyStatementSettings(stmt); //执行doInStatement方法 T result = action.doInStatement(stmt); this.handleWarnings(stmt); //赋值为var12 var12 = result; } catch (SQLException var10) { //... } finally { //... } //最后返回statementCallback对象 return var12; } 根据上面的代码,可以梳理整个执行流程:
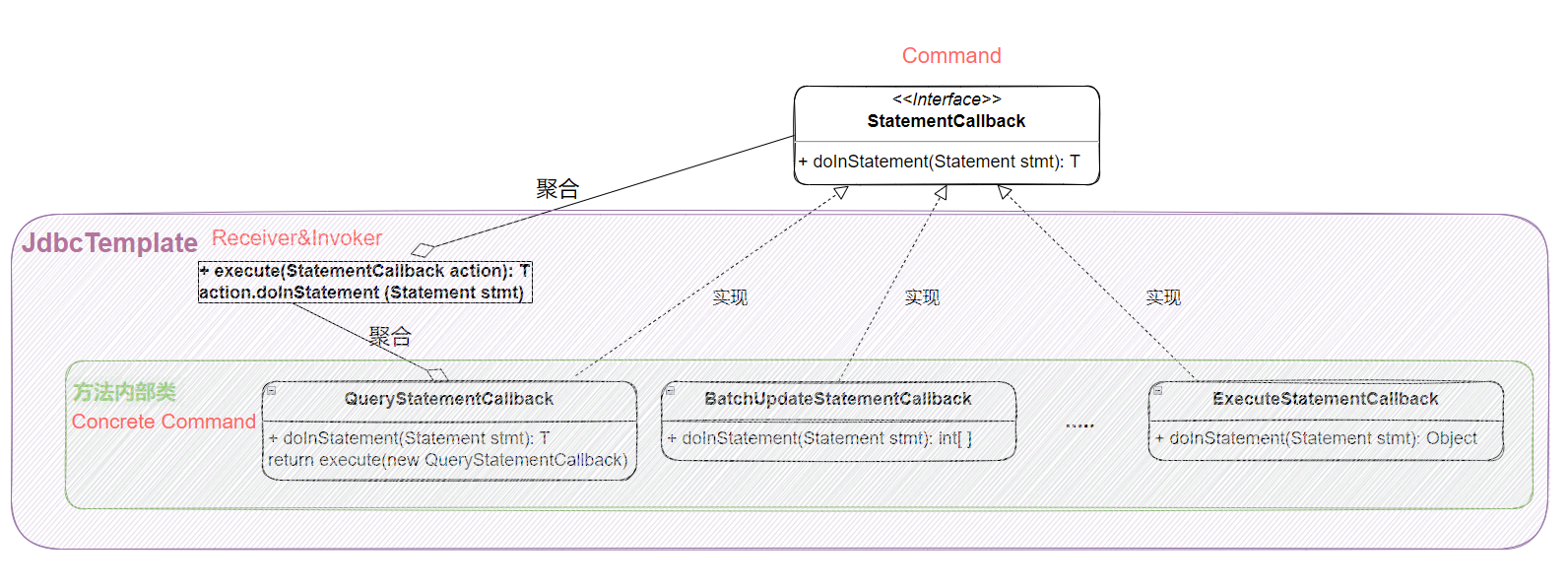
实际上JdbcTemplate这个类是调用者(Invoker)、实现者(Receiver)和具体命令实现(Concrete Command)的集合,statementCallback则是命令的抽象接口。
三、命令模式实战
模拟在餐厅中点餐交给初始烹饪的场景,在该场景中点餐人员只需要把需要点的各种菜系交给服务员,服务员再把各项菜品交给厨师进行烹饪。如下图所示:
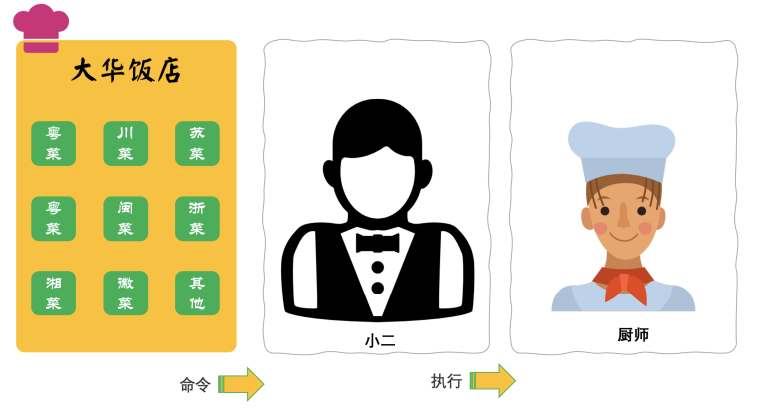
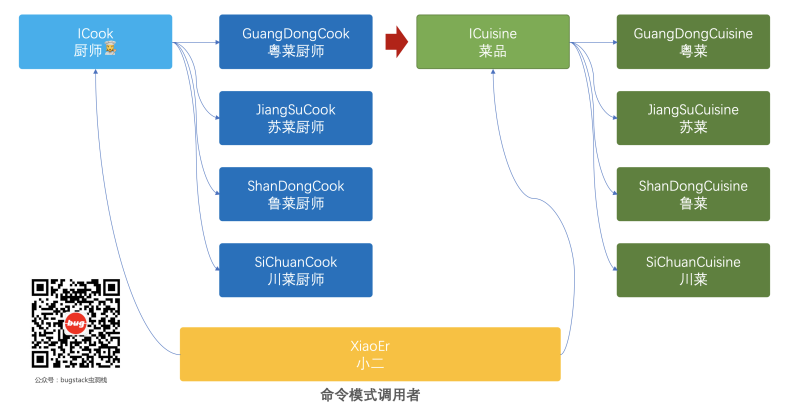
我们先分析一下,命令是菜品具体实现是菜系,命令实现是厨师,调用者是服务员。所以该场景下的命令模式结构应该为:
代码目录结构为:
├─src │ ├─main │ │ ├─java │ │ │ └─cn │ │ │ └─ethan │ │ │ └─design │ │ │ └─command │ │ │ │ Waiter.java │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─cook │ │ │ │ │ ICook.java │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ └─impl │ │ │ │ GuangDongCook.java │ │ │ │ JiangSuCook.java │ │ │ │ ShanDongCook.java │ │ │ │ SiChuangCook.java │ │ │ │ │ │ │ └─cuisine │ │ │ │ ICuisine.java │ │ │ │ │ │ │ └─impl │ │ │ GuangDongCuisine.java │ │ │ JiangSuCuisine.java │ │ │ ShanDongCuisine.java │ │ │ SiChuangCuisine.java │ │ │ │ │ └─resources │ └─test │ └─java │ └─cn │ └─ethan │ └─disign │ ApiTest.java具体代码如下:
- 抽象命令者及其具体实现
/** * @description: 抽象命令接口(八大菜系) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public interface ICuisine { /**烹调公共接口*/ void cook(); } /** * @description: 具体命令实现(广东菜) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class GuangDongCuisine implements ICuisine { private ICook cook; public GuangDongCuisine(ICook cook) { this.cook = cook; } @Override public void cook() { cook.doCooking(); } } /** * @description: 命令具体实现(江苏菜) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class JiangSuCuisine implements ICuisine { private ICook cook; public JiangSuCuisine(ICook cook) { this.cook = cook; } @Override public void cook() { cook.doCooking(); } } /** * @description: 具体命令实现(山东菜) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class ShanDongCuisine implements ICuisine { private ICook cook; public ShanDongCuisine(ICook cook) { this.cook = cook; } @Override public void cook() { cook.doCooking(); } } /** * @description: 具体命令实现(四川菜) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class SiChuangCuisine implements ICuisine { private ICook cook; public SiChuangCuisine(ICook cook) { this.cook = cook; } @Override public void cook() { cook.doCooking(); } }- 抽象实现者及其具体实现
/** * @description: 抽象实现者接口 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public interface ICook { /**厨师烹调*/ void doCooking(); } /** * @description: 具体实现者(广东厨师) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class GuangDongCook implements ICook { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GuangDongCook.class); @Override public void doCooking() { logger.info("广东厨师,会做广东菜"); } } /** * @description: 具体实现类(江苏厨师) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class JiangSuCook implements ICook { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JiangSuCook.class); @Override public void doCooking() { logger.info("江苏厨师,会烧江苏菜"); } } /** * @description: 具体实现类(山东厨师) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class ShanDongCook implements ICook { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ShanDongCook.class); @Override public void doCooking() { logger.info("山东厨师会烧山东菜"); } } /** * @description: 具体实现类(四川厨师) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class SiChuangCook implements ICook { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SiChuangCook.class); @Override public void doCooking() { logger.info("四川厨师会烧四川菜"); } }- 调用者及客户端
/** * @description: 调用者(服务员) * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class Waiter { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Waiter.class); private List cuisineList = new ArrayList<>(); public void order(ICuisine cuisine) { cuisineList.add(cuisine); } public synchronized void placeOrder() { for (ICuisine cuisine : cuisineList) { cuisine.cook(); } cuisineList.clear(); } } /** * @description: 客户端 * @author: wjw * @date: 2022/4/5 */ public class ApiTest { @Test public void test_command() { //菜和厨师命令实现 ICuisine guangDongCuisine = new GuangDongCuisine(new GuangDongCook()); ICuisine shanDongCuisine = new ShanDongCuisine(new ShanDongCook()); ICuisine siChuangCuisine = new SiChuangCuisine(new SiChuangCook()); ICuisine jiangSuCuisine = new JiangSuCuisine(new JiangSuCook()); //调用者进行点单 Waiter waiter = new Waiter(); waiter.order(guangDongCuisine); waiter.order(shanDongCuisine); waiter.order(siChuangCuisine); waiter.order(jiangSuCuisine); //下单操作 waiter.placeOrder(); } } 最终测试结果如下:
23:16:40.512 [main] INFO c.e.d.c.cook.impl.GuangDongCook - 广东厨师,会做广东菜 23:16:40.518 [main] INFO c.e.d.command.cook.impl.ShanDongCook - 山东厨师会烧山东菜 23:16:40.518 [main] INFO c.e.d.command.cook.impl.SiChuangCook - 四川厨师会烧四川菜 23:16:40.518 [main] INFO c.e.d.command.cook.impl.JiangSuCook - 江苏厨师,会烧江苏菜参考资料
《重学Java设计模式》
http://c.biancheng.net/view/1380.html